India’s steel sector is grappling with the dual challenge of meeting growing domestic demand while significantly reducing its carbon emissions. As part of the strategy to decarbonize the sector, green hydrogen offers a transformative solution. The whitepaper on the Role of Green Hydrogen in Indian Steel Sector explores how green hydrogen can decarbonize steel production, address economic feasibility, and assess the growing demand of green hydrogen that will come up considering India’s Net Zero targets.
Emission Reductions through Green Hydrogen Integration
Green hydrogen offers a versatile solution for decarbonizing steelmaking, with applications across various stages of production including agglomeration, blast furnace operations, direct reduced iron (DRI) processes, reheating and galvanizing. Among these, its integration into the gas-based DRI-EAF route holds the greatest potential for emission reductions, making it the most effective pathway for India’s green steel transition.
The table below highlights the impact of green hydrogen adoption across different steelmaking routes:
| Process | GH₂ Usage (kg/ton steel) | Initial CO₂ Emissions (tCO₂e/ton) | CO₂ Emissions after GH₂ Use (tCO₂e/ton) | Emission Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gas-based DRI-EAF | ~65 kg | 1.37 | 0.65 | ~53% |
| BF-BOF | ~14 kg | 2.33 | 2.14 | ~8% |
| Scrap-EAF | ~4 kg | 0.68 | 0.64 | ~5.4% |
| Rotary Kiln DRI-EAF (coal-based) | ~4 kg | 2.25 | 2.21 | ~1.6% |
Demand Growth and Cost Trends
Green hydrogen-based steelmaking is expected to become a major part of India’s transition to a low-carbon economy. The demand for green hydrogen in the steel sector is projected to grow at a 13% CAGR, reaching ~15 MMTPA by FY70. While the current production cost of green hydrogen is USD 7/kg in 2024, the price is expected to decrease significantly, dropping to USD 1.8-2/kg by 2040. This reduction in cost, driven by technological advancements and economies of scale, will make green hydrogen more competitive with traditional methods, accelerating its adoption.
Infrastructure and Resource Requirements
The large-scale deployment of green hydrogen requires substantial investments in production infrastructure. Technologies like Alkaline and Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) electrolysis must be prioritized for scaling up hydrogen production. Additionally, India needs to develop hydrogen storage, distribution networks and integrate renewable energy into steel production to ensure a reliable, sustainable supply of green hydrogen. Alongside these technical advancements, a supportive policy framework is critical to drive these investments and make green hydrogen more affordable.
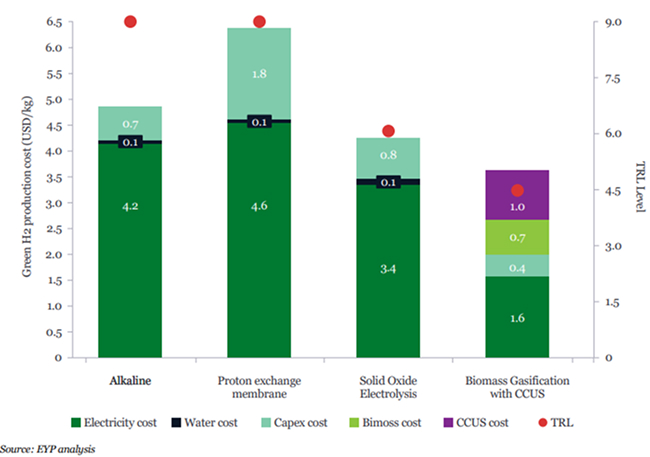
Hydrogen production cost and their technological readiness level (TRLs).
Conclusion
Green hydrogen represents a key opportunity for decarbonizing India’s steel industry, enabling substantial reductions in carbon emissions and supporting the growth of green steel. As costs decrease and infrastructure improves, green hydrogen will become an increasingly competitive alternative to traditional steelmaking methods. Through strategic investments in infrastructure, technology and supportive policies, India can transition to green steel production.

